Shoulder arthrosis is a widespread chronic disease associated with damage to articular structures. The pathological process is accompanied by degenerative deformation of the articular surfaces. At this time, not only cartilage tissue, but also bone tissue is damaged. Pathology symptoms and treatment methods depend on the degree of joint damage.
The disease can develop without showing itself for several years. At some point, under the influence of negative factors (hypothermia, trauma, severe accompanying illness), the first signs of the disease appear. It is at this time that it is necessary to consult a doctor, because the fight against dystrophic changes in the cartilage is especially effective at the beginning of the disease.
Causes of shoulder arthrosis
The causes of degenerative-dystrophic joint tissue damage are numerous and diverse. Among them, injuries play a key role, so post-traumatic arthrosis of the shoulder joint is considered the most common form of pathology. It can also be provoked by mild but repeated damage to cartilaginous tissues.
In addition, the disease can occur under the influence of the following pathological factors:
- Severe joint injuries: synovitis, gout, acute or chronic arthritis, aseptic necrosis of the humerus.
- Regular overloading of the joints. It is most often seen in volleyball, tennis, and basketball athletes.
- Congenital pathology of the shoulder joint.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Old age and old age.
- Overweight (obesity).
- Avitaminosis.
- Autoimmune lesions and weakening of the immune system.
- genetic predisposition.
Most of the patients are people engaged in monotonous physical labor. Therefore, arthrosis of the right shoulder joint is diagnosed more often than the left.
The disease usually develops under the influence of not one, but several negative factors. Based on this, the treatment should be comprehensive and should be aimed not only at fighting the disease, but also at eliminating all the causes that lead to it.
Characteristic symptoms of the disease
Shoulder arthrosis, starting noticeably and gradually developing, can appear suddenly after injury, hypothermia or serious physical exertion. In this case, there are symptoms characteristic of damage to the shoulder joints and nearby tissues:
- pain;
- crackling and clicking during hand movement;
- stiffness and decreased range of motion in the shoulder.
The disease occurs most often in a chronic form. Aggravation of the disease can occur with excessive stress on the joint or injury.
The intensity of the manifestation of symptoms mainly depends on the severity of cartilage and bone tissue damage, so it is customary to distinguish several degrees of the disease. Such a systematization significantly simplifies the diagnosis and allows to accurately predict the outcome of the disease.
Shoulder arthrosis I degree
During this period, the tissues of the joint are slightly affected. Pain is observed very rarely and only after excessive physical exertion or long-term monotonous work. The patient often does not pay attention to these symptoms, associating them with overwork or muscle tension. 1 degree defeat is treated only by conservative methods.
At the beginning of the disease, no obvious changes in the cartilage tissue are observed on radiographs, only an oval ring is noted around the joint cavity.
Shoulder arthrosis II degree
At this stage, the symptoms of the disease are more pronounced. Cartilage tissues are thin and deformed, intra-articular ligaments are damaged. During the movement of the hand, a crunch is heard, the inner layer of the articular bag is inflamed. Over time, the pain becomes constant. Morning stiffness and limited movement appear, which can lead to muscle atrophy.
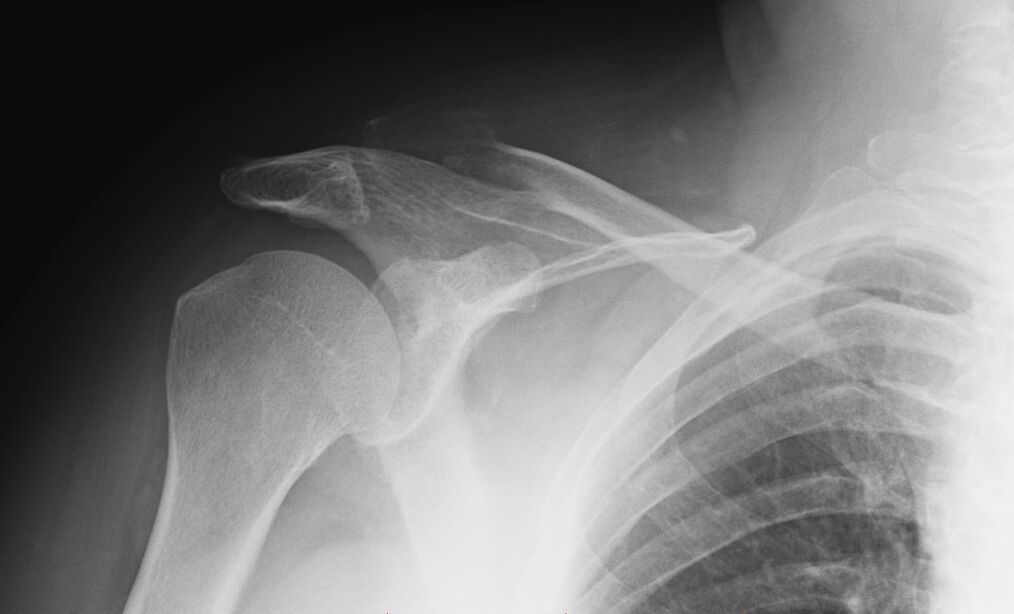
Shoulder arthrosis III degree
During this period, the joint is already significantly deformed, there is practically no movement in it. The patient suffers from sharp pain that can spread to the arm and shoulder blade. If you do not stop the further destruction of tissues, the pathological process can lead to disability.
Third-degree disease is not amenable to conservative treatment and requires surgical intervention.
Shoulder arthrosis rarely reaches the third phase. Often, the transition to the second stage chronic form is diagnosed.
Which doctor should be consulted?
Often people who experience joint pain do not know who to turn to. At the first signs of the disease, you should consult a rheumatologist. The specialist will not only conduct a complete physical examination and make a diagnosis, but also, if necessary, relieve severe pain with an intra-articular injection of anesthesia.
With an advanced form of the disease, there is a possibility that the rheumatologist is powerless. In this case, you will need a surgeon or orthopedist. In big cities, you can only make an appointment with an arthrologist who deals with joint diseases.
How to deal with shoulder arthritis
After medical examination and diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a special therapy that allows to achieve a long and stable remission of the disease. It is impossible to treat degenerative changes in the joints, but it is quite possible to slow down the progress of the destructive process and alleviate the patient's condition.
The main goal of antiarthrosis therapy is to relieve pain and restore joint mobility.
Modern drug treatment
In some patients, it is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis at the initial stage of the disease. At this stage, the pain is not pronounced and does not force patients to seek help from specialists. Often they are treated independently with folk remedies. Some patients engage in therapeutic exercises to reduce joint pain and stiffness. Medicines prescribed by a doctor are used for the treatment of arthrosis in accordance with the recommended dosage and duration of administration. The most effective drugs are the following groups:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- chondroprotectors;
- corticosteroid drugs;
- non-narcotic analgesics;
- vasodilators;
- muscle relaxants.
For this pathology, many drugs are sometimes prescribed for a long time. Depending on the severity of the disease, drugs are taken orally, used externally, intramuscularly or injected into the cavity of the shoulder joint.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Long-term use of NSAIDs is contraindicated due to side effects from the digestive system.
It is possible to treat the disease with drugs already at the early stage of the development of the pathological process. The course is determined based on the patient's condition and severity of symptoms. As an independent treatment, ointments included in this group are not prescribed. They are used together with similar groups of drugs that are used intramuscularly or orally. Their task is to reduce inflammation and alleviate the patient's condition.
Chondroprotectors
Almost all patients' treatment regimen includes drugs aimed at improving metabolic processes in cartilage tissue. In addition, they increase the flexibility of cartilage. Chondroprotectors have such properties. These drugs differ depending on the main active ingredient:
- hyaluronic acid;
- chondroitin sulfate;
- glucosamine;
- combined funds.
Glucosamine is a substance that plays an important role in the formation of healthy cartilage tissue. Chondroitin sulfate's job is to nourish and cushion the shoulders.
Preparations for monotherapy have proven themselves on the market more than the combination of substances.
The polysaccharide in the intercellular space is hyaluronic acid. In addition, it is able to reduce the sensitivity of receptors that respond to pain. Combined chondroprotectors with several active components have the greatest advantage.
The most effective use of chondroprotectors in the early stages of the disease. The task of the drugs is the synthesis of new cells of healthy cartilage tissue that replaces the damaged tissue. When there is pain and swelling, drugs from this group will be less effective. Therefore, first of all, it is necessary to use anti-inflammatory drugs to alleviate the patient's condition.
In order to achieve the maximum effect, injectable preparations are used for intra-articular or intramuscular administration. The course of treatment with chondroprotectors lasts up to six months, some patients see the first results after 3 months of therapy. It is important to follow some rules in the treatment of such drugs.
With the beginning of the therapy course, physical exertion and stressful situations should be excluded. The patient will get the greatest effect if he starts taking chondroprotectors, improves nutrition and starts physiotherapy exercises. Many patients with arthrosis of the shoulder joint are engaged in Dr. Bubnovsky's method, they perform a set of specially designed exercises to achieve a gradual restoration of the joints or stop the progression of the disease.
Corticosteroid agents
When severe pain appears, if anti-inflammatory drugs do not have a positive effect, corticosteroids are prescribed. Ointments or injections are prescribed to alleviate the patient's condition.
Analgesics
Analgesics are prescribed to reduce pain in the initial stages of the disease.
Compared to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs of this group have a less negative effect on the mucosa of the digestive system.
Having an unexplained anti-inflammatory effect, they effectively fight pain.
Vasodilators
Mandatory means in the treatment of arthrosis are vasodilators. They eliminate vascular spasms, normalize blood flow in the affected area. Many patients complain of the appearance of night pains, which are effectively combated by drugs from this group.
Muscle relaxants
When arthrosis of the shoulder joint is affected, muscle spasms are considered a common phenomenon, which is eliminated by muscle relaxants. When prescribing them, the principle of complexity is observed, they are used together with pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs. If necessary, the minimum dose is initially determined with a gradual increase.
Surgical treatment
The main goal of the operation is to restore the working capacity of the joint and improve the patient's quality of life. If conservative therapy is ineffective, if persistent pain syndrome persists, the joint gradually deforms and the range of motion in it is sharply limited, surgical intervention is indicated for the patient.
The decision on the need for surgical intervention is made by the orthopedist or traumatologist together with the patient. Then, the dimensions of the endoprosthesis and the material from which it will be made are determined. Today, implants are made of titanium and high-strength polymers, with a weight close to a natural joint. Durability and reliability of endoprostheses are not in doubt.
Recovery time
The surgery to replace the affected joint is often uncomplicated. Fixation with a support bandage is required for the first 14 days. Early passive performance of a complex of physical exercises on special devices and devices is allowed. Power loads are allowed after 45-60 days.
Physiotherapy
Any anti-arthritic exercise complex is useful only during remission. Charging is contraindicated if there is an increase in temperature, pain and other symptoms of disease exacerbation.
Exercise therapy should not cause pain or discomfort. Exercise should be abandoned at the slightest discomfort.

Refilling should be done daily. After the load, using a healing cream, it is useful to self-massage in the area of the affected joints and nearby muscles, the attending physician will help you choose.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy allows to increase the effect of drugs, reduce their dosage and minimize the risk of complications. The type of physiotherapy is determined by the doctor based on the patient's condition, neglect of the process and possible contraindications due to accompanying diseases.
The following physiotherapy procedures are often used in the treatment:
- magnetotherapy;
- ultrasound with hydrocortisone;
- electrophoresis with anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents;
- ultraviolet radiation
- laser and infrared treatment.
Physiotherapy is carried out several times a year in courses consisting of 10-15 sessions.
Treatment with folk methods
By combining folk treatment with drug therapy, exercise therapy, proper nutrition and physiotherapy, you can achieve a long and stable remission.
One of the best recipes is a compress using birch leaves, which have anti-inflammatory and warming effects. Young leaves are most suitable, because their beneficial properties decrease near autumn. Before applying the compress, a small massage of the affected limb is necessary. Then the leaves are applied to the skin, reinforced with adhesive film and bandage. The compress is left overnight. The duration of treatment is 10 days.
Salt baths have a healing effect. Before the procedure, the crystals are pre-dissolved in hot water. Then the resulting solution is poured into the bath. About 3 kg of salt is needed for the procedure. In addition, you can add a few drops of any essential oil. It is good to take a bath before going to bed, the duration of the bath should not exceed 30 minutes.
A warm oat compress helps a lot. They should be poured with boiling water, insisted and used as intended. It is recommended to do such procedures at night.
Less useful plant hills. Crushed plants with anti-inflammatory effect (yarrow, ginger, turmeric, cinquefoil, calamus) are brewed with boiling water, kept under the lid for 10 minutes and applied to the painful area. After the procedure, the affected shoulder should be smeared with a healing cream and go to bed.
It is recommended to take an infusion of corn stigmas inside. A teaspoon of raw materials or 1 filter bag is brewed with 200 ml of boiling water, insisted for 30 minutes under the lid and 1 tablespoon is consumed. spoon half an hour before meals.
Prevention of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint
Prevention of the disease can be primary and secondary. Primary prevention includes the following measures:
- regular exercise - jogging or brisk walking, exercises for the muscles of the shoulder girdle;
- cold and hot shower;
- elimination of overloads and prevention of traumatic situations.
- timely treatment of diseases that can cause shoulder arthrosis;
Secondary prevention focuses on early diagnosis and treatment of arthritis.
The result
Restoring joint functions is a long and difficult process. Treatment of shoulder arthrosis should be aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease first. Only complex therapy combining medical and folk methods will bring relief and restore working capacity.













































